AI Discovery
We asked ourselves: where can AI be most impactful in genomic drug discovery? The answer was clear. AI has an incredible ability to summarize vast datasets, see connections humans can't, and make predictions from complex data. A single gene like PCSK9 has over 20,000 phenotypic and molecular associations in Inference. This would take months for an analyst to review, but AI can do it in seconds.

Embeddings
The map of causal human biology.
VB-Atlas learns embeddings from tens of thousands of association studies to create a map of relationships between genes and phenotypes. It finds connections in the data itself, not by mining literature or what's already been published.
Query any gene and instantly find others with similar association profiles. Explore relationships that span disease areas and molecular mechanisms. Navigate biological space in ways that were never possible with isolated studies.
Dense embeddings make massive datasets immediately accessible to language models, enabling powerful AI-driven discovery.
Entyvio (vedolizumab) is an α4β7 integrin antagonist for IBD. We mapped the ITGA4 subunit in VB-Atlas to identify new IBD targets: 5 of the top 10 similar gene clusters hit known IBD GWAS regions, including CEBPB, a novel target with clear QTL-based variant-to-gene mapping and existing oncology inhibitors that could be repurposed.
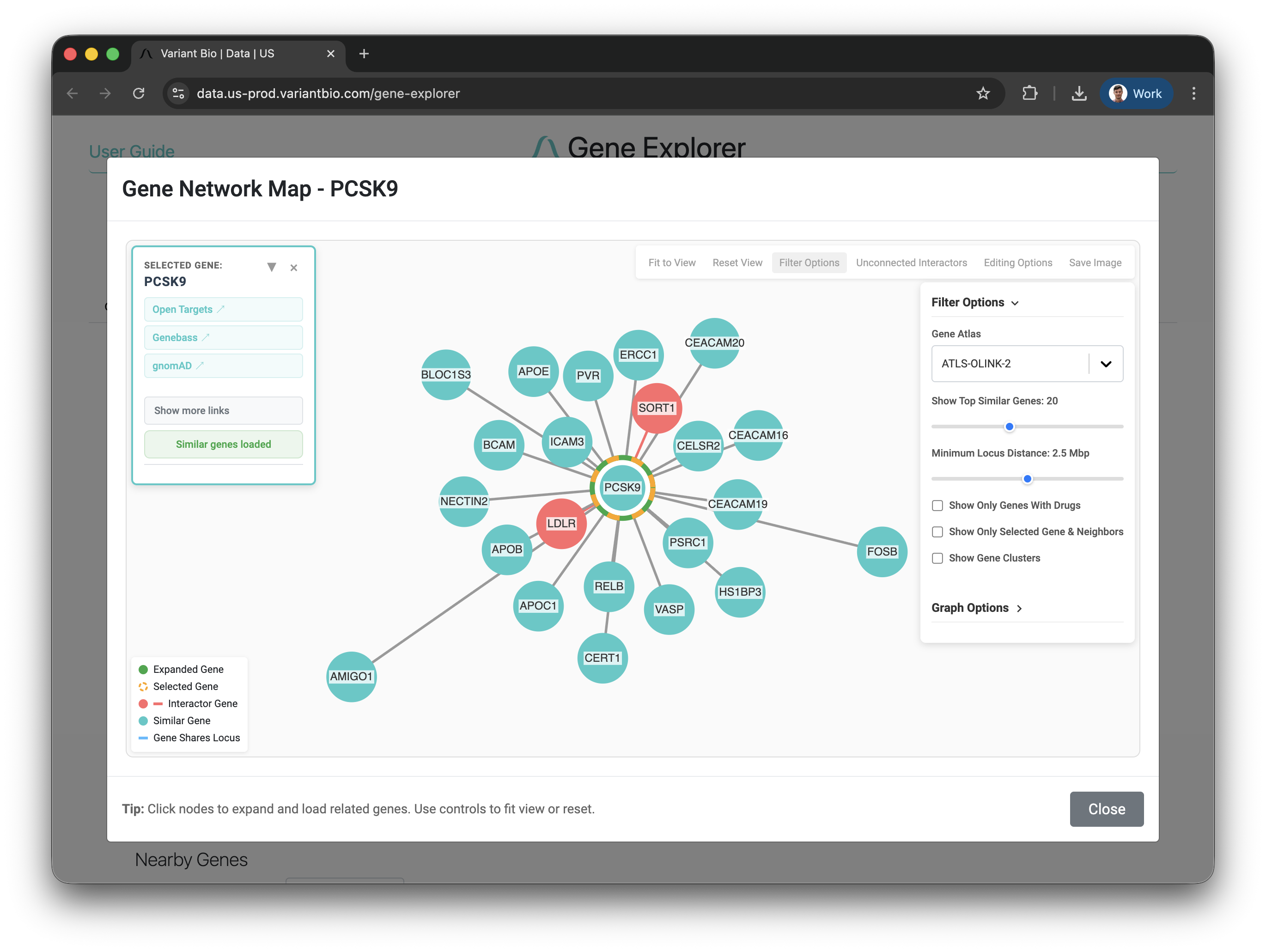
Querying PCSK9 reveals genes with similar association profiles across thousands of studies. Each cluster represents genes that behave similarly across phenotypes, potential alternative targets or pathway members.
Predictive Models
Molecular models that see what clinicians can't.
VB-Predict creates molecular models of disease using proprietary transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data combined with neural networks.
These models predict clinically relevant traits from multi-omic data, dramatically expanding the therapeutic area scope of every study. Apply a model trained in one cohort across entirely different populations. Identify the molecular features most predictive of disease outcomes. Discover novel biomarkers and targets.
The ELF score is a clinically validated marker of fibrosis, but expensive to measure. We built a model to predict ELF from proprietary proteomic data, applied it to 38,000 UK Biobank participants, ran a GWAS, and replicated known fibrosis loci while discovering new ones.
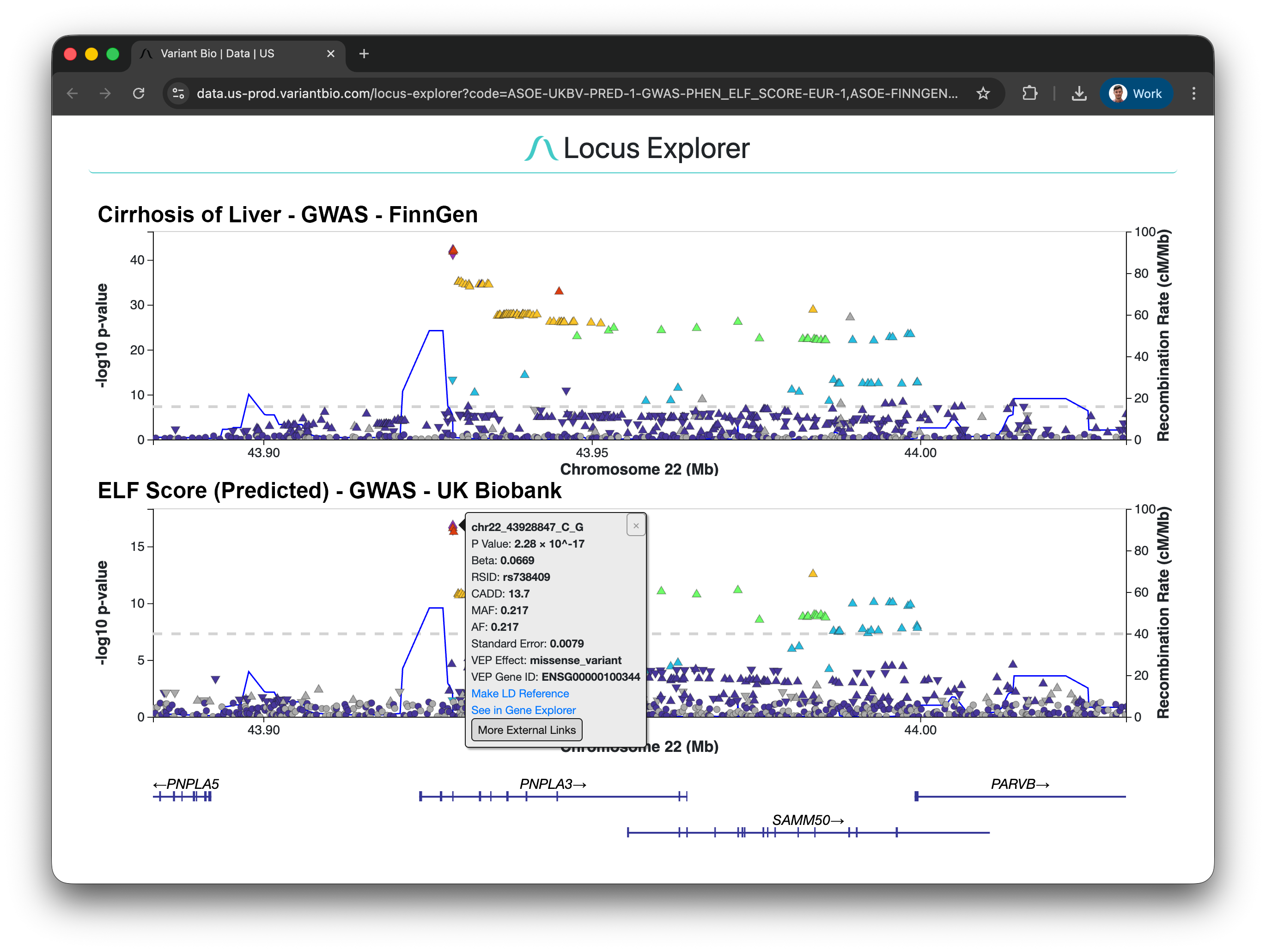
Locus Explorer comparing a liver cirrhosis GWAS from FinnGen (top) with a GWAS of predicted ELF score from UK Biobank proteomics (bottom). The well-known PNPLA3 missense variant is highlighted, validating that VB-Predict captures real biology.
Learn how Inference can accelerate your research and transform your drug discovery pipeline.
Contact Us →